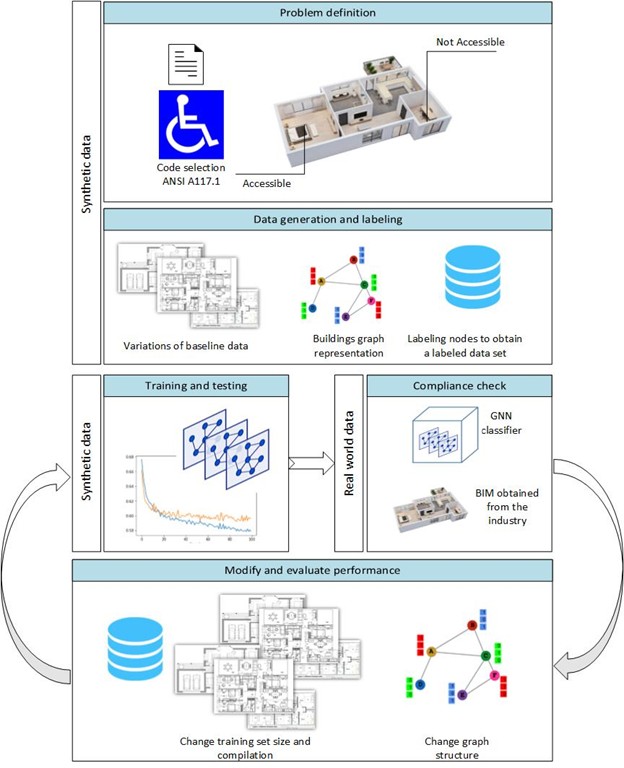
ML for Automated Code Checking (ACC)
Most research efforts for automated code compliance checking focus on improving the existing, well established, rule-based approach. The underlying goal of these efforts is to generate a computer readable representation of the regulations and the design, to enable the comparison between the two. The extensive amount of effort for translating regulations written by human experts for the use of human experts, into machine readable rules, and for preprocessing of the BIM models so that they contain all necessary information for code checking, hinder the ability to cover a wide range of regulatory requirements and reach full automation in the checking process. Moreover, matching of the concepts represented in the computer readable regulations to those represented in the computer readable design remains a challenging task that is highly reliant on human understanding.
Our work extends beyond the commonly used rule base methods into the realm of AI and Machine Learning. We have demonstrated the abilities of ML to support ACC tasks and explored their strengths and weaknesses. We continue to explore the applicability of a variety of ML approaches (supervised learning, graph-based learning, computer vision) to support ACC.
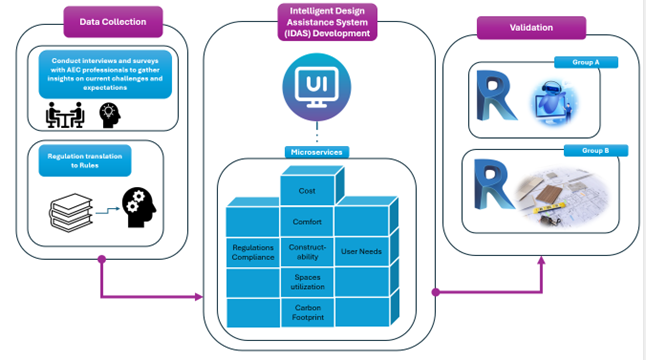
Intelligent Design Assistance System
Design modeling is an iterative process requiring extensive revisions. Current practices rely on static code-checking tools and post-design validation, which extend project timelines, inflate costs, and compromise design quality. These limitations highlight the need for innovative tools that deliver immediate feedback during modeling.
Real-time design assistance offers a promising solution to these challenges, providing immediate insights to designers during the modeling process. Such systems can streamline compliance with regulatory standards, optimize designs for performance and sustainability, and align outputs with user preferences. The technological foundation for such systems is bolstered by advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and virtual reality (VR), enabling the development of intelligent solutions that seamlessly integrate into design workflows.
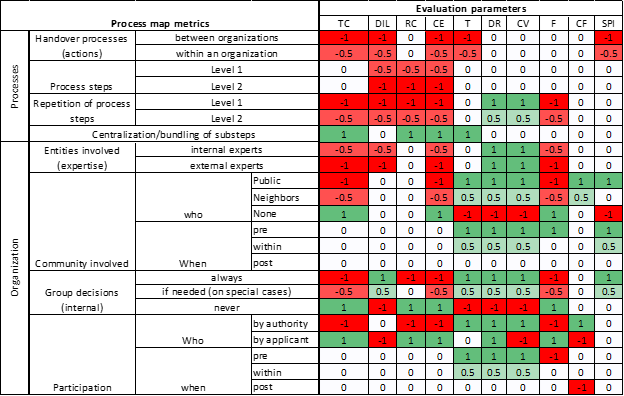
Digitalization and automation of the building permitting process
With the recent technological development and its impact on the construction sector, the interest in streamlining the permitting process through digitalization grows. Looking at building permitting from a construction management and process management perspective is an important approach to address efficiency improvement. In addition to the actual checking of substantial requirements for the building (content check), formal requirements must also be compared. These include, for example, a completeness check of documents, the assignment of responsible employees, the obtaining and evaluation of third-party opinions, and the issuing of the notification letter. Interestingly, many of these procedures which collectively comprise the entire permitting process are usually investigated individually.
We aim to lay the foundations for a holistic view of digitalization of the permitting process, striving for deeper understanding of the existing workflows to enable a systematic comparison across different countries. This will serve as a solid foundation for change and improvement.
Uncertainty management in construction
Design uncertainty is a multifaceted issue in construction projects, impacting all stages of construction. While some researchers have addressed this topic, much of the work has been indirect, and there remains a lack of clarity on applying uncertainty management methods effectively. Our research aims to explore what constitutes uncertainty, how it can be quantified, and how it affects various phases of the construction process.


